|
|
Sndgems jewelry guides are easy to use, interesting and helpful guide to buying jewelry onle. Our jewelry guides are indispensable guide to judging jewelry characterstics, distinguishing genuine from imitation, making wise choices, useful to all type of consumers, from professional jewelry to online searchers. Our diamond guides help everyone in viewing diamonds as gemologists, diamond experts, diamond dealers, experienced lapidaries,
diamond buyers and online customers. Our diamond guides dissects each aspect of diamond value in detail with a wealth of diamond grading information. Our gemstone guides help everyone in viewing colored gemstones as gemologists, gem dealers, experienced lapidaries, gem buyers and online customers. Our gemstone guides dissects each aspect of ruby, sapphire, ruby value in detail with a wealth of gemstone grading information. Our guides offers step-by-step instructions for how to examine
and judge the quality and craftsmanship and materials even if you dont know anything about jewelry. If you're thinking of buying jewelry online this guide is a best place to start. Our guides will help you to know about jewelry details such as finishes, settings, flaws and fakes. Our guides cover diamonds, gemstones, jewelry craftsmanship, treatments, diamond and gems sources, appraisals. There is something for everyone.
Gemstones Buying Guides, Expert Advice, Online Gemstone Shopping Tips
Welcome to the dazzling world of gemstones! You will find out all the shiny
details about gem stones, what type of gemstones can be found out there and how
from dusty hard rocks they transform into that precious shiny ring necklace or
pendant in your nearby jewelry store.
Gems have intrigued human beings for more than 10,000 years. This stones were reserved for wealthy and served as status symbols. A prior knowledge of gemstones (ruby, emerald and sapphire) will help you understand and retain what a jeweler tells you. This gemstone guide will help you in evaluating the quality of ruby, emerald and sapphire, an aid in avoiding fraud with information on immitation (synthetic and treatment), as a handy reference on colored gemstones, provide a collection of practical tips on choosing and caring for gems and a challenge to view colored gemstones through the eyes of gemologists and gem dealers. When gemologists speak of shape, they usually mean its face up outline. The most common gemstone shapes include round, oval, square, pears, marquise and octogon.
Precious gems are generally rare and have deep vivid colors. Only three gems
are winning candidates for the title of “precious”: the vivid green jade, the
deep mysterious blue sapphire and the passionate red ruby. Because natural high
quality precious gems are very rare, the jewelry industry will usually use
additional chemical processes to enhance the color, clarity of the stones or
even synthetically create them so they can be proudly inserted into creative
pieces various budgets can buy.
The most precious, worldwide known and desired is of course, the diamond, a
symbol for eternal shine and strength and according to popular culture: “a
girl’s best friend”. To assess the value of precious gemstones, specialists
evaluate according to the so called “4 Cs”: color, cut clarity and carat
weight. For colorless diamonds, the cut and the carat weight would be the
determining factors in assessing their high value whereas for the other precious
gems the quality of their color is one of the most important factors in
determining their worth.
Precious gemstones come from all over the world, but there are various
regions that are very well known for their precious gem: Brazil is one of the
largest exporters of amethysts, certain African countries such as Sierra Leone
are well known for the bountiful supply of diamonds and for some economies in
the world, precious gem stone trade accounts for almost 30% of their trade
volume.
Their rarity and increased value has generated throughout history various
mythical interpretations that are associated with each gemstone. From antique
beliefs that gems have healing powers to the modern association between one’s
birth month and a specific gem there have been numerous mystical accounts people
have created to add powerful dimensions to the rarity and preciousness of
gems.
Whether you are just dazzled by their beauty, or interested in how they are
valued and processed or just intrigued by their mythical stories click on the
above tabs for more information!More commonly known as gems, gemstones are pieces of minerals used in the art
of making jewelry. They are usually colored, either opaque or transparent and
according to their worth gems can be considered precious and semi-precious.
American Gemological Society: Since 1934, American Gem Society (AGS) has been protecting the
consumers. For 70 years, the AGS logo has been a symbol of excellence in the
jewelry industry. As an association of fine jewelers, our members are committed
to the highest ethics, and practice truth-in-advertising and pricing. To visit
AGS website click here. AGS is
located at 181 World Trade Center, 2050 Stemmons Expressway, Dallas, TX 75027
and their telephone number is 809-972-1162.
Enhancement is often
used as another word for treatment. Enhancement also refers to the faceting and
polishing of a gem. For centuries, ruby, emerald and sapphire have been in heat
treated to improve their color. Heat treating is widely accepted because it is a
continuation of a natural process and it causes a permanent improvement of the
entire gemstone. From the standpoint of value, it does not matter whether
commercially-quality stones have been treated or not as long as the color is
permanent. The overall quality of the treated stone will determine the price.
However, a premium may be charged for high-quality untreated stones that comes
with a lab report stating there is no evidence of heat treatment.
The "celestial" sapphire,
symbol of the heavens, bestower of innocence, truth, good health, and preserver
of chastity, is reserved today as the birthstone of September.
|
Sapphire was named after the Greek word "sapphirus", meaning
blue. The striking deep blue of a quality sapphire is reminiscent of a cloudless
night sky. Ancient civilizations believed that the world was set upon an
enormous sapphire, which painted the sky blue with its reflection. In ancient
times, Sapphires were thought to be protective against envy, and even against
poisoning. A common belief was that a venomous snake placed in a Sapphire
vessel would rapidly die! Ground to a powder, the blue stone was believed to
cure colic, rheumatism and mental illness, and to strengthen
eyesight.
|
|
Sapphire has long symbolized truth, sincerity, and
faithfulness. The Tradition holds that Moses was given the ten commandments on
tablets of sapphire, making it the most sacred gemstone. Because sapphires
represent divine favor, they were the gemstone of choice for kings and high
priests. The British Crown Jewels are full of large blue sapphires, and even
more recently Prince Charles chose a sapphire engagement ring for Princess
Diana. The ancients regarded star sapphires as a very powerful talisman, a
guiding star for travelers and seekers of all kinds.
|
The word "ruby" derives
from the Latin word rubeus, which means red. Ruby is the name given to the red
variety of corundum.
|
The word Ruby comes from the Latin "ruber," meaning red..It has
been said that the Ruby's red glow comes from an internal flame that cannot be
extinguished, making a gift of this stone symbolic of everlasting love. With
its hardness and durability, it is a perfect engagement gem. And if worn on the
left hand, ancient lore has it that the Ruby will bring good fortune to its
wearer, too! Ruby has been the world's most valued gemstone for thousands of
years. Ruby was said to be the most precious of the twelve stones God created
when he created all things, and this "lord of gems" was placed on Aaron's neck
by God's command.
|
|
In the Bible, Job says that �wisdom is more precious than
rubies� Rubies were thought to represent heat and power. Ancient tribes used
the gem as bullets for blowguns, and it was said that a pot of water would boil
instantly if a Ruby was tossed into it. Ground to powder and placed on the
tongue, this crystal was used as a cure for indigestion. Among the multitude of
legends and strange beliefs of ancient times, it was thought that the wearer of
a ruby was blessed with health, wealth, wisdom and outstanding success in`heart
affairs '.Furthermore, the wearer acquired the ability to live in peace with his
enemies. In some places ruby was even thought to confer invulnerability. Rubies
are today even more valuable and rare than the top quality colorless diamonds. A
16 carat ruby was sold at auction for US$ 227,300 per carat at Sotheby's in
1988.
|
|
The name emerald is a derivative of an ancient Persian word,
coming to us through the corruption of the Latin `Smaragdus'. The history of the
emerald is as fascinating as it is voluminous. The ancients prized it as the
symbol of love, rebirth and eternal youth. Because the rich green color of
emerald reminds of spring, it has been treasured for at least the past 4,000
years by different cultures all around the world. Cleopatra reportedly valued
her emeralds more than any other gem, and with good cause as the ancient
Egyptians revered them as symbols of fertility and rebirth.
|
|
The Romans believed that emeralds with a pale hue were immature
and would grow to a deeper, richer colour with age. The ancient Roman scholar
Pliny was so moved by the emerald's lush colour he wrote, �nothing is more
intense than the green of emerald� and �sight is refreshed and restored by
gazing upon this stone�. Following his advise, Roman emperor Nero wore emerald
sunglasses to watch the gladiators. Emerald is said to give a supernatural
ability to foretell future events. A surprising variety of virtues have been
ascribed to emerald. Among these, emerald was thought to improve its owner�s
memory and eloquence, and was also said to quicken intelligence. In a particular
instance of emerald�s use, as a measure against ills, women wearing the stone
were believed to be immune from epilepsy.
|
Shape of Gemstone
The facet gemstone have several shapes. Some is normal but some shapes can not be found in normal gem market because some shape is cut from the imagine of cutter. It is mean that is the unique shape. But the gemstone and diamond shapes chart below is the standard shapes that offer in gem market around the world.
Emerald cut
Emerald cut is a rectangular or square step cut with diagonal corners. It has approximately 50 facets.
Oval cut
Oval cut is a modified brilliant cut with an obround shaped girdle outline. The oval cut has an elliptical shape when viewed from the top. It has approximately 69 facets.
Radiant cut
Radiant cut is a rectangular cut, combining the shape of an emerald cut and sparkle of a brilliant. It has approximately 70 facets.
Pear or Teardrop cut
Pear or Teardrop cut is asymmetrical cut with one pointed and one rounded end. A hybrid cut, combining the best of the oval and the marquise, it is shaped like a sparkling teardrop. It has approximately 71 facets.
Cushion cut
Cushion cut is looks like a cross between a deep cut with large facets that was common in the late 19th and the early 20th centuries and a modern
Marquise cut
Marquise cut is a symmetrical boat shaped brilliant cut gem with pointed ends. It has approximately 57 facets.
Old miner cut
Old miner cut is also more of a square or cushion cut, rather than being round. In fact, today's cushion cut is an improved old mine cut.
Trillion cut
Trillion cut is a triangular shape. It has approximately 44 facets.
Heart cut
Heart cut is a pear shape with a cleft at the top. It has approximately 59 facets.
Asscher cut
Asscher cut is a square cut characterized by a smaller table and larger step facet than an emerald cut.
Flanders cut
Flanders cut is an octagon, but when viewed from above it looks like a square. In reality it has four short sides and four long sides. This cut also includes 61 facets
Princess cut
Princess cut is technically known as “Square Modified Brilliant” and is a square version of the round brilliant cut with numerous sparkling facets. It has approximately 76 facets.
Round cut
Round cut is the name implies, it is round on top. It has approximately 57 facts.
Gemstones Specific Gravity, Mohs Hardness, Index of Refraction
Learn all about gemstones properties like Specific Gravity, Mohs Hardness, Index of Refraction as it will help in identifying genuine gemstone from fake stones, evaluating gemstone quality and source of origin.
| Gemstone Name |
Specific Gravity |
Mohs Hardness |
Index of Refraction |
Gemstone Family |
| Achorite |
3.03 - 3.25 |
7.0 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.610-1.661 |
Tourmaline |
| Agate |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.530 - 1.550 |
Quartz |
| Alexandrite |
3.68 - 3.78 |
8.5 Mohs |
1.746 - 1.755 |
Chrysoberyl |
| Almandine |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.750 - 1.830 |
Garnet |
| Almandine Spinel |
3.58 - 4.06 |
8.0 Mohs |
1.708 - 1.735 |
Spinel |
| Almandine-Spessartine |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.750 - 1.830 |
Garnet |
| Amazonite |
2.55 - 2.76 |
6.0 - 6.5 Mohs |
1.518 - 1.526 |
Feldspar |
| Amethyst |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.532 - 1.554 |
Quartz |
| Andradite |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.880 - 1.940 |
Garnet |
| Aquamarine |
2.63 - 2.91 |
7.5 - 8.0 Mohs |
1.567-1.590 |
Beryl |
| Balas Ruby |
3.58 - 4.06 |
8.0 Mohs |
1.708 - 1.735 |
Spinel |
| Black Opal |
1.98 - 2.25 |
5.5 - 6.5 Mohs |
1.440 - 1.460 |
Opal |
| Bloodstone |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.535 - 1.539 |
Quartz |
| Brazilian Emerald |
3.03 - 3.25 |
7.0 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.610 - 1.640 |
Tourmaline |
| Cairngorm |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.540 - 1.550 |
Quartz |
| Carnelian |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.530 - 1.550 |
Quartz |
| Cat's Eye |
3.68 - 3.78 |
8.5 Mohs |
1.746 - 1.755 |
Chrysoberyl |
| Chalcedony |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.544 - 1.553 |
Quartz |
| Chlorspinel |
3.58 - 4.06 |
8.0 Mohs |
1.712 - 1.717 |
Spinel |
| Chrome Pyrope |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.730 - 1.760 |
Garnet |
| Chrysoberyl |
3.68 - 3.78 |
8.5 Mohs |
1.746 - 1.755 |
Chrysoberyl |
| Chrysoprase |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.530 - 1.550 |
Quartz |
| Citrine |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.532 - 1.554 |
Quartz |
| Color-Change Garnet |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.730 - 1.760 |
Garnet |
| Demantoid |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.880 - 1.900 |
Garnet |
| Diamond |
3.51 |
10 Mohs |
2.417 |
Diamond |
| Dravite |
3.03 - 3.25 |
7.0 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.610-1.661 |
Tourmaline |
| Emerald |
2.63 - 2.91 |
7.5 - 8.0 Mohs |
1.560 - 1.605 |
Beryl |
| Feldspar |
2.55 - 2.76 |
6.0 - 6.5 Mohs |
1.518 - 1.572 |
Feldspar |
| Fire Opal |
1.98 - 2.25 |
5.5 - 6.5 Mohs |
1.430 - 1.460 |
Opal |
| Garnet |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.730 - 1.760 |
Garnet |
| Ghanospinel |
3.58 - 4.06 |
8.0 Mohs |
1.712 - 1.747 |
Spinel |
| Goshenite |
2.63 - 2.91 |
7.5 - 8.0 Mohs |
1.570 - 1.600 |
Beryl |
| Green Quartz |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.540-1.550 |
Quartz |
| Grossular |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.880 - 1.940 |
Garnet |
| Heliodore |
2.63 - 2.91 |
7.5 - 8.0 Mohs |
1.570 - 1.600 |
Beryl |
| Heliotrope |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.535 - 1.539 |
Quartz |
| Hessonite |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.730 - 1.760 |
Garnet |
| Hyacinth |
4.60 - 4.70 |
7.5 Mohs |
1.777 - 1.987 |
Zircon |
| Indicolite |
3.03 - 3.25 |
7.0 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.610 - 1.640 |
Tourmaline |
| Jade |
2.90 - 3.10 |
6.0 Mohs |
1.640 - 1.667 |
Jade |
| Jadeite |
2.90 - 3.10 |
6.0 Mohs |
1.640 - 1.667 |
Jade |
| Jargon |
4.60 - 4.70 |
7.5 Mohs |
1.777 - 1.987 |
Zircon |
| Jasper |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.540 - 1.550 |
Quartz |
| Labradorite |
2.55 - 2.76 |
6.0 - 6.5 Mohs |
1.560 - 1.572 |
Feldspar |
| Lapis Lazuli |
2.70 - 2.90 |
5.0 - 5.5 Mohs |
1.500 - 1.550 |
Lapis Lazuli |
| Malaia |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.880 - 1.940 |
Garnet |
| Matura Diamond |
4.60 - 4.70 |
7.5 Mohs |
1.777 - 1.987 |
Zircon |
| Moonstone |
2.55 - 2.76 |
6.0 - 6.5 Mohs |
1.518 - 1.526 |
Feldspar |
| Morganite |
2.63 - 2.91 |
7.5 - 8.0 Mohs |
1.585 - 1.594 |
Beryl |
| Morion |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.540 - 1.550 |
Quartz |
| Nephrite |
2.90 - 3.10 |
6.0 Mohs |
1.600 - 1.641 |
Jade |
| Onyx |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.531 - 1.539 |
Quartz |
| Opal |
1.98 - 2.25 |
5.5 - 6.5 Mohs |
1.440 - 1.460 |
Opal |
| Orthoclase |
2.55 - 2.76 |
6.0 - 6.5 Mohs |
1.518 - 1.526 |
Feldspar |
| Peridot |
3.22 - 3.45 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.635 - 1.690 |
Peridot |
| Peristerite |
2.55 - 2.76 |
6.0 - 6.5 Mohs |
1.560 - 1.572 |
Feldspar |
| Praziolite |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.540 - 1.550 |
Quartz |
| Pyrope |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.730 - 1.760 |
Garnet |
| Pyrope-Almandine |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.730 - 1.760 |
Garnet |
| Pyrope-Spessartine |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.730 - 1.760 |
Garnet |
| Quartz |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.544 - 1.553 |
Quartz |
| Red Beryl |
2.63 - 2.91 |
7.5 - 8.0 Mohs |
1.570 - 1.598 |
Beryl |
| Rhodolite |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.740 - 1.770 |
Garnet |
| Rock Crystal |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
2.000 |
Quartz |
| Rose Quartz |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.540 - 1.550 |
Quartz |
| Rubellite |
3.03 - 3.25 |
7.0 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.610 - 1.640 |
Tourmaline |
| Rubicelle |
3.58 - 4.06 |
8.0 Mohs |
1.712 - 1.717 |
Spinel |
| Ruby |
3.96 - 4.05 |
9.0 Mohs |
1.757 - 1.779 |
Corundum |
| Sapphire |
3.96 - 4.05 |
9.0 Mohs |
1.757 - 1.779 |
Corundum |
| Sapphire Spinel |
3.58 - 4.06 |
8.0 Mohs |
1.712 - 1.747 |
Spinel |
| Siberite |
3.03 - 3.25 |
7.0 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.625-1.675 |
Tourmaline |
| Smoky Quartz |
2.65 |
7.0 Mohs |
1.540 - 1.550 |
Quartz |
| Spessartine |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.790 - 1.810 |
Garnet |
| Spinel |
3.58 - 4.06 |
8.0 Mohs |
1.712 - 1.717 |
Spinel |
| Sunstone |
2.55 - 2.76 |
6.0 - 6.5 Mohs |
1.560 - 1.572 |
Feldspar |
| Topaz |
3.50 - 3.60 |
8.0 Mohs |
1.607 - 1.627 |
Topaz |
| Topazolite |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.880 - 1.940 |
Garnet |
| Tourmaline |
3.03 - 3.25 |
7.0 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.603 - 1.655 |
Tourmaline |
| Tsavorite |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.739 - 1.744 |
Garnet |
| Turquoise |
2.60 - 2.80 |
5.0 - 6.0 Mohs |
1.610 - 1.650 |
Turquoise |
| Uvarovite |
3.50 - 4.30 |
6.5 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.740 - 1.870 |
Garnet |
| Verdilite |
3.03 - 3.25 |
7.0 - 7.5 Mohs |
1.612-1.638 |
Tourmaline |
| Water Opal |
1.98 - 2.25 |
5.5 - 6.5 Mohs |
1.440 - 1.460 |
Opal |
| White Opal |
1.98 - 2.25 |
5.5 - 6.5 Mohs |
1.440 - 1.460 |
Opal |
| Zircon |
4.60 - 4.70 |
7.5 Mohs |
1.777 - 1.987 |
Zircon |
Gemstone's specific gravity
Specific gravity, the abbreviated is SG, is the meatured that comparing about the gemstone's weight when weighted in the air with weighted suspennded in pure water. Because specific gravity varies with chemical composition and crystal structure type.The specific gravity is a ratio which can be used for indentifying gemstones. But this method can not be used for identified gemstone alone. But the specific gravity can help in reducing the amount kind of gemstone of possibilities. Learn all about gemstones properties like Specific Gravity, Chemical Composition and Crystal Stucture as it will help in identifying genuine gemstone from fake stones, evaluating gemstone quality and source of origin.
The table below is the list gemstone's specifict gravity that arranged from the gemstone in increasing order.
|
Gemstone
type
|
Specific
gravity
|
Chemical
Composition
|
Crystal
Structure
|
|
Amber
|
1.05 –
1.10
|
Oxygenated hydrocarbon
(variable)
|
Amorphous
|
|
Chrysocolla
|
1.9 –
2.4
|
Hydrous copper
silicate
|
Monoclinic
|
|
Opal ex. Fire opal,
Moss opal, Doublet opal and Boulder opal
|
1.98 –
2.5
|
Hydrous silicon
dioxide
|
Amorphous
|
|
Hackmanite
|
2.14 –
2.40
|
Sodium aluminum silicate
chloride
|
Cubic
|
|
Sodalite
|
2.14 –
2.40
|
Sodium aluminum silicate
chloride
|
Cubic
|
|
Tourmaline
ex. Rubellite, Paraiba, Chrome etc.
|
2.28 –
3.32
|
Silicate compounded with
aluminium, iron, magnesium, sodium, lithium, or
potassium.
|
Trigonal
|
|
Turquoise
|
2.31 –
2.84
|
Hydrated copper aluminum
phosphate
|
Triclinic
|
|
Moldavite
|
2.32 –
2.38
|
Silicon dioxide + aluminum
oxide
|
Amorphous
|
|
Hambergite
|
2.35
|
Beryllium
borate
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Obsidian
|
2.35 –
2.60
|
Siliceous glassy
rock
|
Amorphous
|
|
Variscite
|
2.42 –
2.58
|
Hydrous aluminum
phosphate
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Serpentine
|
2.44 –
2.62
|
Basic magnesium
silicate
|
Microcrystalline
|
|
Howlite
|
2.45 –
2.58
|
Calcium borosilicate
hydroxide
|
Monoclinic
|
|
Lapis
lazuli
|
2.5 -
3
|
Sodium calcium aluminum
silicate
|
Cubic
|
|
Maw sit
sit
|
2.5 –
3.5
|
Rock containing variable amounts
of kosmochlor, jadeite and albite
|
Rock
|
|
Jasper
|
2.5 –
2.9
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Charoite
|
2.54 –
2.78
|
Complex silicate containing
phosphorus, calcium, and sodium
|
Monochinic
|
|
Seraphinite
|
2.55 –
2.75
|
Magnesium iron aluminum silicate
hyroxide
|
Monochinic
|
|
Amazonite
|
2.56 –
2.58
|
Potassium aluminum
silicate
|
Triclinic
|
|
Orthoclase
|
2.56 –
2.58
|
Potassium aluminum
silicate
|
Monochinic
|
|
Moonstone
|
2.56 –
2.59
|
Potassium aluminum
silicate
|
Monochinic
|
|
Scapolite
|
2.57 –
2.74
|
Sodium calcium aluminium
silicate
|
Tetragonal
|
|
Chrysophase
|
2.58 –
2.64
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Bloodstone
|
2.58 –
2.64
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Agate
& Carnelian
|
2.58 –
2.64
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Peanut
wood
|
2.58 –
2.91
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Rose quartz cat’s
eye
|
2.58 –
2.64
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Hexagonal
|
|
Chalcedony
|
2.58 –
2.64
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Tiger’s
eye
|
2.58 –
2.64
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Iolite
|
2.58 –
2.66
|
Magnesium aluminum
silicate
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Coral
|
2.6 –
2.7
|
Calcium
carbonate
|
Trigonal
|
|
Pietersite
|
2.6
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Aggregate
|
|
Fossil
coral
|
2.6 –
2.7
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Agate
geode
|
2.6 –
2.64
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Pearl
|
2.6 –
2.85
|
Calcium
carbonate
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Sunstone
|
2.62 –
2.65
|
Sodium calcium aluminium
silicate
|
Triclinic
|
|
Aventurine
|
2.64 –
2.69
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Quartz
|
2.65
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Strawberry
quartz
|
2.65
|
Silocon dioxide with iron oxide
inclusions
|
Trigonal
|
|
Amethyst
|
2.65
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Quartz ex. Rose,
Smoky, Cat’s eye and Mystic
|
2.65
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Labradorite
|
2.65 –
2.75
|
Sodium calcium aluminum
silicate
|
Triclinic
|
|
Citrine
|
2.65
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Hexagonal
|
|
Rutile
quartz
|
2.65
|
Silicon dioxide with titanium
inclusions
|
Trigonal
|
|
Ametrine
|
2.65
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Onyx
|
2.65 –
2.91
|
Silicon
dioxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Andesine
labradorite
|
2.66 –
2.68
|
Sodium calcium aluminum
silicate
|
Triclinic
|
|
Beryl ex. Morganite,
Goshenite etc
|
2.66 –
2.87
|
Aluminium beryllium
silicate
|
Hexagonal
|
|
Emerald
|
2.66 –
2.87
|
Aluminium beryllium
silicate
|
Hexagonal
|
|
Aquamarine
|
2.66 –
2.87
|
Aluminium beryllium
silicate
|
Hexagonal
|
|
Calcite
|
2.69 –
2.71
|
Calcium
carbonate
|
Trigonal
|
|
Larimar
|
2.74 –
2.88
|
Hydrated sodium calcium silicate
with manganese
|
Triclinic
|
|
Ammolite
|
2.75 –
2.80
|
Mainly aragonite (with calcite,
silica and pyrite)
|
Amorphous
|
|
Sugilite
|
2.76 –
2.80
|
Potassium sodium lithium iron
manganese aluminium
|
Hexagonal
|
|
Verdite
|
2.76 -
3
|
Serpentine
rock
|
Monoclinic
|
|
Lepidolite
|
2.8 –
2.9
|
Potassium lithium aluminum
silicate hydroxide fluo
|
Monoclinic
|
|
Prehnite
|
2.82 –
2.94
|
Basic calcium aluminum
silicate
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Jadeite
|
2.90 –
3.03
|
Basic calcium magnesium iron
silicate
|
Monoclinic
|
|
Nephrite
jade
|
2.9 –
3.03
|
Calcium magnesium iron
silicate
|
Monoclinic
|
|
Danburite
|
2.97 –
3.03
|
Calcium boric
silicate
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Nuumite
|
3
|
Rock containing gedrite and
anthophyllite
|
Lamellar fibrous
structure
|
|
Fluorite
|
3
– 3.25
|
Calcium
fluoride
|
Cubic
|
|
Andalusite
|
3.05 –
3.20
|
Aluminium
silicate
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Clinohumite
|
3.13 –
3.75
|
Magnesium
silicate
|
Monoclinic
|
|
Spodumene ex. Kunzite
|
3.15 –
3.21
|
Lithium aluminum
silicate
|
Monoclinic
|
|
Apatite
|
3.16 –
3.23
|
Basic fluoro- and chloro-calicum
phosphate
|
Hexagonal
|
|
Hiddenite
|
3.17 –
3..19
|
Lithium aluminum
silicate
|
Monoclinic
|
|
Diopsie ex. Chrome, Tashmarine and
star
|
3.22 –
3.38
|
Calcium magnesium
silicate
|
Monoclinic
|
|
Sillimanite
|
3.23
|
Aluminum
silicate
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Malachite
|
3.25 –
4.10
|
Basic copper
carbonate
|
Monoclinic
|
|
Dumortierite
quartz
|
3.26 –
3.41
|
Aluminum borate silicate
intergrown with quartz
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Axinite
|
3.26 –
3.360
|
Calcium aluminum borate
silicate
|
Triclinic
|
|
Peridot
|
3.28 –
3.48
|
Magnesium iron
silicate
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Hemimorphite
|
3.3 –
3.5
|
Hydrous basic zinc
silicate
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Diaspore or Zultanite
|
3.30 –
3.39
|
Hydrated aluminum
oxide
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Idocrase
|
3.32 –
3.47
|
Complex calcium aluminum
silicate
|
Tetragonal
|
|
Ruby -
Zoisite
|
3.35
|
Rock containing zoisite, ruby and
hornblende
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Tanzanite
|
3.35
|
Calcium aluminium
silicate
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Rhodonite
|
3.40 –
3.74
|
Manganese
silicate
|
Triclinic
|
|
Rhodochrosite
|
3.45 –
3.70
|
Manganese
carbonate
|
Trigonal
|
|
Topaz ex. Rutile,
Mystic, Azotic, imperial etc.
|
3.49 –
3.57
|
Aluminum
fluorsilicate
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Sphene
|
3.52 –
3.54
|
Calcium titanium
silicate
|
Monoclinic
|
|
Kyanite
|
3.53 –
3.70
|
Aluminum
silicate
|
Triclinic
|
|
Spinel
|
3.54 –
3.63
|
Magnesium aluminium
oxide
|
Cubic
|
|
Grossular garnet
ex. Grossularite and Mali
|
3.57 –
3.73
|
Calcium aluminum
silicate
|
Cubic
|
|
Tsavorite
Garnet
|
3.57 –
3.73
|
Calcium aluminum
silicate
|
Rhombic
|
|
Garnet ex. Pyrope
and Color Change Garnet
|
3.62 –
3.87
|
Magnesium aluminum
silicate
|
Cubic
|
|
Star
garnet
|
3.62 –
3.87
|
Iron aluminum
silicate
|
Rhombic
|
|
Hessonite
Garnet
|
3.64 –
3.69
|
Calcium aluminum
silicate
|
Cubic
|
|
Demantoid
Garnet
|
3.7 –
4.1
|
Calcium iron
silicate
|
Cubic
|
|
Melanite
|
3.7 –
4.1
|
Calcium iron
silicate
|
Cubic
|
|
Chrysoberyl
|
3.70 –
3.78
|
Beryllium aluminium
oxide
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Alexandrite
|
3.70 –
3.78
|
Beryllium aluminium
oxide
|
Orthorhombic
|
|
Azurite
|
3.7 –
3.9
|
Basic Copper
Carbonate
|
Monoclinic
|
|
Gaspeite
|
3.71
|
Nickel magnesium iron
carbonate
|
Trigonal
|
|
Rhodolite
Garnet
|
3.85
|
Magnesium aluminum
silicate
|
Cubic
|
|
Sphalerite
|
3.9 –
4.1
|
Zinc
sulphide
|
Cubic
|
|
Almandite
Garnet
|
3.93 –
4.30
|
Iron aluminium
silicate
|
Cubic
|
|
Zircon
|
3.93 –
4.73
|
Zirconium
silicate
|
Tetragonal
|
|
Sapphire
|
3.95 –
4.03
|
Aluminium
oxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Ruby
|
3.97 –
4.05
|
Aluminum
oxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Smithsonite
|
4.00 –
4.65
|
Zinc
carbonate
|
Trigonal
|
|
Spessartite
Garnet
|
4.12 –
4.18
|
Manganese aluminium
silicate
|
Cubic
|
|
Rainbow
pyrite
|
5
– 5.2
|
Iron
sulphide
|
Cubic
|
|
Hematite
|
5.12 –
5.28
|
Iron
oxide
|
Trigonal
|
|
Cassiterite
|
Gemstone's Refractive Index
Refracive index, the abbreviated is RI, is one of the most important identified of gemstone. Because almost gemstones will have different refractive index, but not all. So if you have to make sure what stone you test, you have to used other method with also. Whatever the refractive index testing have to be the one method you can not deny.
When light passes from one density or type of material (air) into another (the gemstone), it is bent or "refracted." The amount, or degree, that the beam of light is bent will be determined by the density difference between the air and the gem. The measurement used to quantify the amount that a light beam is bent in a given material is known as its "refractive index".
There are two factors when calculating a gem's refractive index: "angle of incident" and "refractive angle." The "incident angle" is the angle of the approaching light as it intersects with the stone's exterior surface. The "refractive angle" is the altered angle of the light as it passes through the stone's interior. The Refractive Index is the ratio of difference between these two angles. Each material has its own unique density and Refractive Index.
The color of a gemstone, and the frequency (color) of the light traveling through it, can also effect its refractive index. As the light's frequency changes, so does its angle of refraction. Higher light frequencies travel through the stone more slowly, while lower frequencies travel faster, causing a spreading effect known as dispersion. As each frequency is reflected it is dispersed throughout the stone's interior at varying speeds and directions. As the scattering and dispersion of light within the stone is increased, so to is the amount of "fire" that is returned to the viewer.
The color of a gemstone, and the frequency (color) of the light traveling through it, can also effect its refractive index. As the light's frequency changes, so does its angle of refraction. Higher light frequencies travel through the stone more slowly, while lower frequencies travel faster, causing a spreading effect known as dispersion. As each frequency is reflected it is dispersed throughout the stone's interior at varying speeds and directions. As the scattering and dispersion of light within the stone is increased, so to is the amount of "fire" that is returned to the viewer. Learn all about gemstones properties like Refractive Index, Double Refraction, Birefringence as it will help in identifying genuine gemstone from fake stones, evaluating gemstone quality and source of origin.
The table below is the list gemstone's RI that arranged from the gemstone that have the lowest refractive index to highest refractive index.
|
Gemstone
|
Refractive
index
|
Double
Refraction
|
Birefringence
|
|
Opal
|
1.37 –
1.52
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Fluorite
|
1.434
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Obsidian
|
1.45 –
1.55
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Chrysocolla
|
1.469 –
1.57
|
Yes
|
0.023 -
0.040
|
|
Moldavite
|
1.48 –
1.54
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Sodalite
|
1.48
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Hackmanite
|
1.48
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Calcite
|
1.486 –
1.658
|
Yes
|
0.172
|
|
Coral
|
1.486 –
1.658
|
Yes
|
White and red : 0.160 –
0.172
|
|
Lapis
lazuli
|
1.5
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Moonstone
|
1.518 –
1.526
|
Yes
|
0.008
|
|
Orthoclase
|
1.518 –
1.53
|
Yes
|
0.008
|
|
Ammolite
|
1.52 –
1.68
|
Yes
|
0.155
|
|
Pearl
|
1.52 –
1.69
|
Yes
|
0.156
|
|
Maw sit
sit
|
1.52 –
1.74
|
Yes
|
0.015 –
0.02
|
|
Amazonite
|
1.522 –
1.530
|
Yes
|
0.008
|
|
Lepidolite
|
1.525 –
1.586
|
Yes
|
0.029 –
0.038
|
|
Sunstone
|
1.525 –
1.548
|
Yes
|
0.010
|
|
Agate
|
1.53 –
1.54
|
Yes
|
0.001 –
0.004
|
|
Bloodstone
|
1.53 –
1.54
|
Yes
|
0.001 –
0.004
|
|
Carnelian
|
1.53 –
1.54
|
Yes
|
0.001 –
0.004
|
|
Quartz ex. Rose, Smoky and
Lemon
|
1.53 –
1.54
|
Yes
|
0.009
|
|
Fossil
coral
|
1.53 –
1.54
|
Yes
|
0.001 –
0.004
|
|
Chrysophase
|
1.53 –
1.54
|
Yes
|
0.004 –
0.009
|
|
Chalcedony
|
1.53 –
1.54
|
Yes
|
0.001 –
0.004
|
|
Tiger’s
eye
|
1.534 –
1.540
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Quartz cat’s
eye
|
1.534 –
1.540
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Amber
|
1.539 –
1.545
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Scapolite
|
1.540 –
1.579
|
Yes
|
0.006 –
0.037
|
|
Peanut
wood
|
1.54
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Jasper
|
1.54
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Iolite
|
1.542 –
1.578
|
Yes
|
0.008 –
0.012
|
|
Aventurine
|
1.53 –
1.54
|
Yes
|
0.009
|
|
Pietersite
|
1.544 –
1.553
|
Yes
|
0.009
|
|
Ametrine
|
1.544 –
1.553
|
Yes
|
0.009
|
|
Mystic
quartz
|
1.544 –
1.553
|
Yes
|
0.009
|
|
Onyx
|
1.544 –
1.553
|
Yes
|
0.001 –
0.004
|
|
Rutile
quartz
|
1.544 –
1.553
|
Yes
|
0.009
|
|
Amethyst
|
1.544 –
1.553
|
Yes
|
0.009
|
|
Citrine
|
1.544 –
1.553
|
Yes
|
0.009
|
|
Charoite
|
1.550 –
1.561
|
Yes
|
0.004 –
0.009
|
|
Andesine
labradorite
|
1.551 –
1.560
|
Yes
|
0.008
|
|
Verdite
|
1.552 –
1.576
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Hambergite
|
1.553 –
1.628
|
Yes
|
0.007
|
|
Labradorite
|
1.559 –
1.570
|
Yes
|
0.008 –
0.010
|
|
Serpentine
|
1.560 –
1.710
|
Yes
|
0.008 –
0.014
|
|
Morganite
|
1.562 –
1.602
|
Yes
|
0.004 –
0.010
|
|
Beryl
|
1.562 –
1.620
|
Yes
|
0.004 –
0.010
|
|
Goshenite
|
1.562 –
1.620
|
Yes
|
0.004 –
0.010
|
|
Veriscite
|
1.563 –
1.594
|
Yes
|
0.031
|
|
Aquamarine
|
1.564 –
1.596
|
Yes
|
0.004 –
0.005
|
|
Emerald
|
1.565 –
1.602
|
Yes
|
0.006
|
|
Seraphinite
|
1.576 –
1.599
|
Yes
|
0.005 –
0.011
|
|
Howlite
|
1.586 –
1.605
|
Yes
|
0.019
|
|
Larimar
|
1.595 –
1.645
|
Yes
|
0.038
|
|
Rhodochrosite
|
1.6 –
1.82
|
Yes
|
0.208 –
0.220
|
|
Nephrite
jade
|
1.600 –
1.627
|
Yes
|
0.027
|
|
Jadeite
|
1.600 –
1.627
|
Yes
|
0.027
|
|
Sugilite
|
1.607 –
1.611
|
Yes
|
0.001 –
0.004
|
|
Topaz
|
1.609 –
1.643
|
Yes
|
0.008 –
0.016
|
|
Gaspeite
|
1.61 –
1.81
|
Yes
|
0.22
|
|
Turquoise
|
1.61 –
1.65
|
Yes
|
0.04
|
|
Prehnite
|
1.611 –
1.699
|
Yes
|
0.021 –
0.039
|
|
Hemimorphite
|
1.614 –
1.636
|
Yes
|
0.022
|
|
Tourmaline ex. Chrome, cat’s
eye, rubellite, Paraiba and indicolite
|
1.614 –
1.666
|
Yes
|
0.014 –
0.032
|
|
Smitsonite
|
1.621 –
1.849
|
Yes
|
0.228
|
|
Andalusite
|
1.627 –
1.649
|
Yes
|
0.007 –
0.013
|
|
Apatite
|
1.628 –
1.649
|
Yes
|
0.002 –
0.006
|
|
Clinohumite
|
1.629 –
1.674
|
Yes
|
0.029 –
0.045
|
|
Danburite
|
1.630 –
1.636
|
Yes
|
0.006 –
0.008
|
|
Peridot
|
1.650 –
1.703
|
Yes
|
0.036 –
0.038
|
|
Malachite
|
1.655 –
1.909
|
Yes
|
0.254
|
|
Silimanite
|
1.655 –
1.684
|
Yes
|
0.014 –
0.021
|
|
Axinite
|
1.656 –
1.704
|
Yes
|
0.010 –
0.012
|
|
Spodumene ex. Kunzite,
Hiddenite
|
1.660 –
1.681
|
Yes
|
0.014 –
0.016
|
|
Diopside ex. Chrome, star and
Tashmarine
|
1.664 –
1.730
|
Yes
|
0.024 –
0.031
|
|
Dumotierite
quartz
|
1.678 –
1.689
|
Yes
|
0.015 –
0.037
|
|
Ruby -
Zoisite
|
1.691 –
1.700
|
Yes
|
0.009
|
|
Tanzanite
|
1.691 –
1.700
|
Yes
|
0.009
|
|
Idocrase
|
1.700 –
1.732
|
Yes
|
0.002 –
0.012
|
|
Diaspore or refer to
Zultanite
|
1.702 –
1.750
|
Yes
|
0.048
|
|
Kyanite
|
1.710 –
1.734
|
Yes
|
0.015 –
0.033
|
|
Spinel
|
1.712 –
1.762
|
|
|
|
Rhodonite
|
1.716 –
1.752
|
Yes
|
0.010 –
0.014
|
|
Azurite
|
1.720 –
1.848
|
Yes
|
0.108 –
0.110
|
|
Garnet ex. Pyrote, Star,
Rhodolite, Color change and Hessonite
|
1.720 –
1.756
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Grossular garnet ex. Tsavorite,
Grossularite and Mali
|
1.734 –
1.759
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Chrysoberyl
|
1.746 –
1.763
|
Yes
|
0.004 –
0.010
|
|
Alexandrite
|
1.746 –
1.763
|
Yes
|
0.004 –
0.010
|
|
Corundum ex. Sapphire, Ruby
|
1.762 –
1.778
|
Yes
|
0.008
|
|
Garnet ex. Almandite and
Spessartite
|
1.77 –
1.82
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Zircon
|
1.810
-2.024
|
Yes
|
0.002 –
0.059
|
|
Sphene
|
1.843 –
2.110
|
Yes
|
0.100 –
0.192
|
|
Melanite
|
1.88 –
1.94
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Andradrite garnet ex. Demantoid
and Topazolite
|
1.88 –
1.94
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Cassiterite
|
1.997 –
2.098
|
Yes
|
0.096 –
0.098
|
|
Sphalerite
|
2.368 –
2.371
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Diamond
|
2.417 –
2.419
|
None
|
N/A
|
|
Hematite
|
2.94 –
3.22
|
Yes
|
0.287
|
Learn all about gemstones properties like Clarity as it will help in identifying genuine gemstone from fake stones, evaluating gemstone quality and source of origin.
Gemstone
clarity
Gemstone clarity
is a quality of gemstone relating to the existence and visual appearance of
internal characteristics of a diamond called "inclusions", and surface
defects called "blemishes".
Inclusions may be crystals of a
foreign material or another gemstone crystal, or structural imperfections such
as tiny cracks that can appear whitish or cloudy. The number, size, color,
relative location, orientation, and visibility of inclusions can all affect the
relative clarity of a gemstone. A clarity grade is assigned based on the overall
appearance of the stone under 10x magnification.
GIA specify gemstone in 3 Type. In
each type, gemstones list is different. So gemstone's quality maybe same but the
gem's inclusion maybe different. So you can check at the chart
below.
Type 1 -
gemstone
|
Type 1 -
gemstones
|
Type 1 -
clarity
|
|
Beryl
Aquamarine
Green
Morganite
Yellow
Chrysoberyl
Green
Yellow
Quartz
Smokey
Spodumene
Kunzite
Green
Topaz
Blue
Yellow
Orange
Pink
Red
Tourmaline
Green
Zircon
Blue
Zoisite
Tanzanite
|
VVS - Very, Very
Slightly Included (the best) Minute inclusions that are difficult to see using
10X, and are not visible at all to the naked eye.
VS - Very
Slightly Included Minor inclusions that are easier to see using 10X, but still
not visible to the naked eye.
SI1 - Slightly
Included I The inclusions are easily seen using 10X, and are noticeable with the
naked eye.
SI2 - Slightly
Included 2 The inclusions are more easily seen using 10X, and are quite visible
with the naked eye.
I1 - Included 1
The inclusions are very obvious and they have a moderate negative effect on the
over-all appearance or durability of the
gemstone.
I2 - Included 2
The inclusions are very obvious and they have a severe negative effect on the
over-all appearance or durability of the
gemstone.
I3 - Included 3
The inclusions are very obvious and they have a severe negative effect on both
the over-all appearance and durability of the
gemstone.
|
Type 2 -
gemstone
|
Type 2 -
gemstones
|
Type 2 -
clarity
|
|
Andalusite
All
Chrysoberyl
Alexandrite
Corundum
All colors (i.e. Sapphire and Ruby)
Garnet
All
species and colors
Iolite -
All
Peridot -
All
Quartz
Amethyst
Citrine
Ametrine
Spinel -
All
Tourmaline
Blue
Orange
Yellow
Multi-colored (except watermelon
color)
Zircon
Green
Orange
Red
Yellow
|
VVS - Very, Very
Slightly Included (the best) Minor inclusions that are somewhat easy to see
using 10X, but still not visible to the naked eye.
VS - Very
Slightly Included Noticeable inclusions that are easier to see using 10X, and
may be slightly visible to the naked eye.
SI1 - Slightly
Included I The inclusions are easily seen using 10X and are large or numerous,
and are noticeable with the naked eye.
SI2 - Slightly
Included 2 The inclusions are easily seen using 10X and are large or numerous,
and are very noticeable with the naked eye.
I1 - Included 1
The inclusions are very obvious and they have a moderate negative effect on the
over-all appearance or durability of the
gemstone.
I2 - Included 2
The inclusions are very obvious and they have a severe negative effect on the
over-all appearance or durability of the
gemstone.
I3 - Included 3
The inclusions are very obvious and they have a sever negative effect on both
the over-all appearance and durability of the
gemstone.
|
Type 1 -
gemstone
|
Type 1 -
gemstones
|
Type 1 -
clarity
|
|
Beryl
Emerald
Tourmaline
Red
Pink
Watermelon (green transitioning to pink or
red)
|
VVS - Very, Very
Slightly Included (the best) Noticeable inclusions that are easy to see using
10X, but usually not visible to the naked eye.
VS - Very
Slightly Included Obvious inclusions that are easy to see using 10X, and usually
visible to the naked eye. SI1 - Slightly Included I The inclusions are large and
numerous using 10X, and prominent with the naked
eye.
SI2 - Slightly
Included 2 The inclusions are large and numerous using 10X, and very prominent
with the naked eye. I1 - Included 1 The inclusions are very obvious and they
have a moderate negative effect on the over-all appearance or durability of the
gemstone.
I2 - Included 2
The inclusions are very obvious and they have a severe negative effect on the
over-all appearance or durability of the
gemstone.
I3 - Included 3
The inclusions are very obvious and they have a sever negative effect on both
the over-all appearance and durability of the
gemstone.
|
For this grading, you will know
some stone's kind in several type grading. So it is mean, different colors in
same gemstone family is not same value amount. Learn all about gemstones properties like Color, Hue, Tone, Intensity as it will help in identifying genuine gemstone from fake stones, evaluating gemstone quality and source of origin.
|
|
GIA color
grading
GIA
color grading is separated to be 3 types. The first one is intensity, or
saturation. The second is hue, or color. And the last is tone, or lightness/
darkness. You can see the picture below for comparing the gem's
colors.
1) Hue
The hue
is the actual color of gemstones ex. red, yellow, green and blue. You can see
the chart below.

2)
Intensity
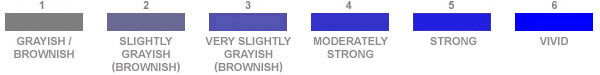
The
gem's intensity, GIA grading in 6 level of saturation ranging by the grey color
saturated of gem color. Please see the chart below.
3) Tone
To describe the
darkness or lightness of a colored stone, the GIA system has 9 levels of tone
ranging from "very very light" to "very very dark." Please see at the chart
below.

With the
exception of hue, each of these parameters by themselves are relatively
meaningless and they must be used in conjunction to tell the full story of a
gem's color quality. Taken together, these three parameters will provide a
simple numeric code that can quickly and accurately quantify gemstone
color.

Example, if you
think about "cornflower" color and "royal blue" color of blue sapphire, you can specify
the color clearly with other when use the GIA color grading chart.
|
Gemstone Inclusions
The next step is to study any inclusions that may be present. If any doubt exists as to whether they are indicative of natural or manmade origin, check the appropriate assignments in the colored gemstone assignments. Inclusions characteristic of synthetic and other manmade stones are to be found also in the supplement with this course. The subject of the use of characteristic inclusions for identification is covered in detail in the assignment following the next work project. At this point, it is important to examine the pattern of inclusions under low power. Often, inclusions that appear to be unrelated individual entities will be seen to form a very revealing pattern when the stone is examined in this manner. For example, in ruby, sapphire and emerald, a number of inclusions or lines that together present a hexagonal aspect may assist materially in identification. The pattern of rutile needles oriented in three directions at 60° to one another in the same plane is a very strong indication of corundum, or at least of the hexagonal crystal system.
Types of Inclusions
Crystals: are solid mineral inclusions of various shapes and sizes. Genuine Ruby and Sapphire will have crystal inclusions like pyrite, garnet, zircon, calcite and spinel. Minute crystals are called pinpoints or grains.
Negative Crystals: are hollow spaces inside a stone that have the shape of a crystal.
Silk: in ruby and sappgire consists of very fine fibers of rutile (titanium oxide) or other minerals. These fibers or rows intersect and rsemble silk. Well formed silk is a good indication that stone has not been heat treated.
Needles: are long, thin inclusions that are either solid crystals or tubes filled with gas or liquid and are called growth tubes.
Fluid Inclusions: are hollow spaces filled with fluid. They occur in random shapes and are sometimes dense creating a milky look. Fluid inclusions are of three types: single phase inclusions with only fluids; two phase inclusions with liquid and gas and three phase with a liquid, a gas and a solid. Type of inclusions can also help in identifying source of the gemstone.
Cracks (Fractures or Fissures); of various sizes are commonly seen in ruby and sapphire. Cracks are also referred to as feathers.
Parting: refers to breakage along a plane of weekness. In ruby and sapphire parting planes are thin seams of boehmite.
Twinning: occurs when two or more crystals of the same mineral are united and are generally seen as straight lines.
Halos: are circular fractures around a crystal and during heating the crystal can expand.
Fingerprints: are very common in ruby and sapphire and are healed cracks and look like human fingerprints.
Saturn: like inclusions have a central core with the shape of flattned sphere surrounded by a planar circular. The core be solid, hollow or fluid and gas. The surface of the core is smooth and metallic or granular like a snowball. Saturn like inclusions are found in rubies from Thailand and Cambodia and are a good indication that helps gemologists determine country of origin.
Growth or Color Zoning: are referred to uneven distribution of color and if color zones look like bands they are called growth or color bands.
Cavities: are holes into a stone from the surface and can be caused during stone cutting process.
Chips: are broken off pieces of stone along the girdle or at the culet.
Now that you are familiar with gemstones properties like Refractive Index, Double Refraction, Birefringence, Specific Gravity, Inclusions it will help in identifying genuine gemstone from fake stones, evaluating gemstone quality and source of origin. The tables below show typical inclusions found in genuine gemstones and fake stones as well as have unique Refractive Index, Double Refraction, Birefringence and other properties. Every gemstone has its own unique identity and genuine gemstone identification is a process that involves identifying gemstones structure and chemical properties. Genuine gemstone identification requires gemological knowlege, gemology tools and a well trained experience eye. There are many ways to identify a real gem from a fake one as well as how to evaluate gemstones quality and its origin.
Characterstics of Genuine Rubies, Sapphires and Emeralds:
| Parameters |
Ruby |
Sapphire |
Emerald |
| Chemical Composition |
Al2O3 |
Al2O3 |
Be3Al2(SiO3)6 |
| Moh's Hardnes |
9 |
9 |
7.5 to 8.0 |
| Specific Gravity |
4.0 |
4.0 |
2.72 |
| Toughness |
Excellent |
Excellent |
Poor to Good |
| Clevage |
None |
None |
Indistinct |
| Parting |
Rhomoohedral |
Rhomoohedral |
-- |
| Fracture |
Uneven |
Uneven |
Uneven |
| Steak |
White or Colorless |
White or Colorless |
White |
| Crystal Symbol |
Hexagonal |
Hexagonal |
Hexagonal |
| Optic Character |
Doubly Refractive |
Doubly Refractive |
Doubly Refractive |
| Refractive Index |
1.765 |
1.765 |
1.578 |
| Birefringence |
.008 to .010 |
.008 to .010 |
.005 - .009 |
| Dispersion |
0.018 |
.018 |
0.014 |
| Luster |
Subadamantine to Vitreous |
Subadamantine to Vitreous |
Vitreous |
| Phenomena |
Asterism (6 to 12 rays), Color Change from Blue to Purple |
Asterism (6 to 12 rays), Color Change from Blue to Purple |
-- |
| Dichroism |
Purplish Red |
Blue Sapphire:Violetish & Greenish BlueYellow Sapphire:Yellow or Greenish YellowOrange Sapphire:Orange or Brownish OrangeGreen Sapphire:Green & Yellow GreenPurple Sapphire:Violet & Orange |
Yellowish Green |
| Chelsea Filter |
Strong Red |
Blackish |
Pink to Red |
| Absorption Spectra |
Fluoroscent at 694 & 693 nm |
Three Bands at 451.5, 460 and 470 nm |
Distinct Lines at 683 and 680.5 nm |
| Color Reason |
Chromium (Iron & Titanium Present Sometimes) |
Blue: Iron & TitaniumYellow: Iron and/or Color CentersOrange: Iron and/or Color CentersGreen: Iron or Iron & TitaniumPurple: Chromium, Iron and Titanium |
Chromium, Vanadium and/or Iron. |
| UV Fluoroscence |
Strong to Weak Red or Orange Red |
Blue: Strong Red to Orange to inert.Yellow: Moderate Orange-Red to inert.Orange: InertGreen: InertPurple: Stong Orange Red |
Usually Inert |
| Heat Reaction |
Turns Green but turns back to Red on cooling. |
|
Additional Fracturing |
| Chemical Reaction |
Highly Resistant |
|
Resistant except Hydroflouric Acid |
| Light Stability |
Stable |
|
Stable |
Characterstics of Facetted Rubies, Sapphires and Emeralds from Finest Mines:
| |
Fluoroscence |
Inclusions |
| Kashmir Sapphire |
Orangy Fluoroscence |
Sharp, Wide Spaced, Straight Zones, Powdry Texture, Glowy Quality |
| Burma Ruby |
-- |
Small Nests like concentrations of tiny rutile needles, color swirls, streamers, calcite and domomite inclusions, graining |
| Buma Sapphire |
-- |
Dense Clouds of rutike silk similar to ruby, silk shorter and more densely packed, fingerprints common, even color and no banding |
| Ceylon Ruby |
-- |
Very Long, fine rutile needles that traverse the whole stne, fingerprints, feathers, negative crystals, uneven coloring, other crystals such as calcite, garnet, pyrite, tourmaline, spinel and apitite. |
| Ceylon Sapphire |
A uniform orange or red fluoroscence |
Very Long, fine rutile needles that traverse the whole stne, fingerprints, feathers, negative crystals, uneven coloring, other crystals such as calcite, garnet, pyrite, tourmaline, spinel and apitite. |
| Thai Ruby |
|
Saturn inclusions which are solid crystals surrounded by fingerprints, no rutile silk, fingerprints wispy like flux inclusions seen in synthetic corrundum, crystals such as pyrrhotite, apitite, garnet, color zoning rare, twinning common, needles which intersect in 3 directions |
| Thai Sapphire |
Inert |
Slightly smilky, no rutile silk, strong and uneven color zoning, white needles, fingerprints, crytals such as feldspar and hornblende |
| Cambodian Sapphire |
Inert |
White boehmoite neddles but no rutile silk, fingerprints and feathers, inclusions with crstal and halo, |
| Australian Sapphire |
Inert |
Crystals like Cambodian Sapphires, fingerprints and feathers, zoning and color banding, |
| Tanzanian Sapphire |
|
Twinning planes and boehmite , tiny thin plats of films |
| Brazalian Emerald |
|
Biotite, dolomite, pyrite crystals, chromite grains, growth tubes |
| Colombian Emerald |
|
Three phase inclusions, jagged borders, gas bubble, halite crystals, albite feldspar, pyrite, calcite |
| Mozambique Emerald |
|
Two phase inclusions, biotite crystals |
| Indian Emerald |
|
Two phase inclusions |
| Pakistan Emerald |
|
Growth tubes, fluid inclusions, chromite, dolomite |
| Tanzanian Emerald |
|
Biotite mica, garnets |
| South African Emerald |
|
Biotite flakes, molybdenite |
| Zambian Emerald |
|
Limonite filled tubes, mucovite mica, tourmaline crystals, hematite platelets, rutile prisms |
Characterstics of Synthetic Rubies and Sapphires:
| Synthetic Ruby & Sapphire |
Spectra |
Fluoroscence |
Chelsea Filter |
Inclusions |
| Verneuil |
Sapphire: No iron lines |
Ruby: Strong Red than both natural and other synthetic rubies
Sapphire:Inert, weak to strong red or orange red
|
Green Sapphire: Red |
Curved growth lines, tiny and large spherical gas bubbles, whitish particles of Al203, small dark red crystals |
| Inamori |
|
Ruby: stronger red than natural
Sapphire Orange: Strong orange red
|
|
Whitish Clouds, gas bubbles, faint growth curved lines, rain like particles |
| Seiko |
|
|
|
Clouds of gas bubbles, swirled and curving growth or color zoning more like foogy Kashmir Sapphire |
| Chatham |
Sapphire: A Diffuse Band at 451.5 nm |
|
|
Platinum plates and needles, white or yellowish flux, seed and accidental crystals |
| Ramaura |
|
small chalky yellow areas, dull, chalky red to orange |
|
Flux inclusions |
Characterstics of Synthetic Emeralds:
| Synthetic Emerald |
Refractive Index |
Birefingence |
Inclusions |
| Kimberly |
1.570 |
0.004 - 0.005 |
Nail head spiculle inclusion with gas and liquid phases, growth features, gold and phenakite crystals, healing fussures |
| Chatham |
1.560 |
0.003 - 0.004 |
Flux fingerprints and veils of whitish, orangy, or brownish flux, platinum, phenakite crystals, parrallel growth planes, two phase gas and liquid inclusions |
| Gilson |
1.565 |
0.005 |
Flux fingerprints and veils of whitish, orangy, or brownish flux, platinum, phenakite crystals, parrallel growth planes, two phase gas and liquid inclusions |
| Linde |
1.560 |
0.003 |
|
| Russian |
1.560 |
0.004 |
Flux fingerprints and veils of whitish, orangy, or brownish flux, platinum, phenakite crystals, parrallel growth planes, two phase gas and liquid inclusions |
Characterstics of High-Quality Sapphires:
| |
Kashmir Sapphire |
Burma Sapphire |
Ceylon Sapphire |
Thai Sapphire |
| Hue |
violetish blue to blue |
violetish blue to blue |
violetish blue to blue, masked by gray |
violetish blue to greenish blue, masked by gray
|
| Tone |
medium to medium dark |
medium dark to very light |
medium dark to very light |
very dark to medium dark |
| Gray Color Masking |
minimum |
minimum |
|
|
| Appearance |
powdery, velvety |
|
|
|
| Color |
looks good in any kind of light but bluest under fluoroscent lighting, color highly saturated due to tone and color purity |
Color more evenly distributed than Kashmir and Ceylon Sapphires, color highly saturated due to tone, color purity and uniform color |
unevenly distributed, the more even the color the better the stone, more brilliance due to lighter color, less saturated than Burma & Kashmir Sapphires due to light tones, gray color masking and uneven color |
lot of black extinctions, more blue less black is more valuable, less saturated than other sapphires |
Characterstics of High-Quality Rubies:
| |
Burma Ruby |
Ceylon Ruby |
Thai Ruby |
| Hue |
orangy red to purplish red to pinkish red |
orangy red to red |
purplish red to orangy red
|
| Tone |
medium to medium dark |
medium to very light |
medium dark to very dark |
| Gray or Brown Color Masking |
no |
|
often masked by gray, brown or black |
| Fluoroscence |
Good red |
Good Red |
Very Little |
| |
|
|
|
| Appearance |
Black extinctions are minimum, stones look red throughout |
Few Dark Extinctions Area due to red fluoroscence and lighter color |
Lot of Black Extinction Areas |
| Color |
Color is highly saturated due to tone, purity of color and fluoroscence, pink overtones, color zoning |
unevenly distributed |
More red and less black the better the stone |
Characterstics of High-Quality Emeralds:
| |
Muzo Mine, Columbia |
Zambian |
Sandawana, Zambia |
| Hue |
bluish green |
strongly blue |
yellowish green
|
| Tone |
medium to medium dark |
medium to medium dark |
medium dark to very dark |
| Gray or Brown Color Masking |
no |
no |
no |
| Color |
Grass Green |
homogenous color |
yellowish green |
Approximate Weight of Cut Round Emeralds, Rubies & Sapphires
| Size |
Emerald |
Ruby & Sapphire |
| 2 mm |
0.04 |
0.04 |
| 3 mm |
0.09 - 0.12 |
0.11 - 0.14 |
| 4 mm |
0.20 - 0.27 |
0.26 - 0.34 |
| 5 mm |
0.40 - 0.48 |
0.52 - 0.63 |
| 6 mm |
0.70 - 0.81 |
0.80 - 1.08 |
| 7 mm |
1.15 - 1.28 |
1.42 - 1.70 |
GIA Ruby Emerald Sapphire Clarity Grades
| VVS |
Very Very Slightly Included - usually invisble to naked eye |
| VS |
Very Slighty Included, sometimes visible to eyes |
| SI1-2 |
Obvious Inclusions, visble to eyes |
| I1 |
Moderate Effect on appearance and durability |
| I2 |
Severe Effect on appearance or durability |
| I3 |
Severe Effect on appearance and durability |
Genuine gemstone identification requires gemological knowlege, gemology tools and a well trained experience eye. There are many ways to identify a real gem from a fake one as well as how to evaluate gemstones quality and its origin. The links below will help you further in getting best deals on genuine gemstones, authentic jewelry and real metals.
|
What is a Genuine Gemstone? Know All About Genuine Gemstones. Read More.
|
|
What is Authentic Jewelry? Know All About Authentic. Read More.
|
|
What is Certified Jewelry? Know All About Certified Jewelry. Read More.
|
|
What is Fine Designer Jewelry? Know All About Fine Jewelry. Read More.
|
|
Genuine Gemstones Identification? Know All About Fine Genuine Gemstones. Read More.
|
|
What is Real Gold, Platinum, Silver, Palladium or Fake Gold Filled, Gold Plated? Know All About Real Gold, Platinum, Silver, Palladium, Platinum, Silver, Palladium. Read More.
|
|
Jewelry Caring & Cleaning, Ruby Jewelry Caring & Cleaning, Sapphire Jewelry Caring & Cleaning, Emerald Jewelry Caring & Cleaning, Diamond Caring & Cleaning. Read More.
|
|
Genuine Diamond Testers, Genuine Gemstones Testers, Real Metal Testers, Authentic Jewelry Testers. ? Know All About Testers to Identify Natural Diamonds, Genuine Gemstones, Real Metals and Authentic Jewelry. Read More.
|
| Sndgems Jewelry Trade Affiliations, Read More and Conflict-Free Diamonds. Read More. |
| Fine-Quality Burma Ruby, Ceylon Ruby, Kashmir Sapphire, Burma Sapphie, Columbian Emerald Guides. Read More. |
| Complete Online Shopping Guide to ensure safe shopping, getting quality value product with money back guarantee when shopping online for jewelry. Read More. |
|
Identification of Synthetic or Fake Emeralds from Genuine Emeralds Guidelines. Read More.
|
|
Identification of Synthetic or Fake Rubies and Sapphires from Genuine Rubies and Sapphires Guides. Read More.
|
| Identification of Ruby, Sapphire Sources - If they're from Burma, Ceylon or Thailand. Read More. |
| Identification of Emerald Sources - If they're from Columbia, Zambia, Brazil, Africa. Read More. |
|

|
| |
|
|
|
|
Gemstone Education
|
|

|
|
|
Diamond Education
|
|

|
|
|
Jewelry Education
|
|

|
|
|
Metals Education
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Settings Education
|
|
|
|
|
Designs Styles Education
|
|

|
|
|
Ring Size Education
|
|

|
|
|
Certification Education
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Authencity Education
|
|

|
|
|
Genuine Gems Education
|
|

|
|
|
Buying Online Education
|
|

|
|
|
Jewelry Care Education
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gems Care Education
|
|

|
|
|
Company Info Education
|
|

|
|
|
Sapphire Jewelry Advice
|
|

|
|
|
Emerald Jewelry Advice
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ruby Jewelry Education
|
|

|
|
|
Antique Jewelry Advice
|
|

|
|
|
Gems Mining Education
|
|

|
|
|
Eco-Friendly Education
|
|

|
|
| Online Shopping Tips - How to Buy Authentic Jewelry, Genuine Gemstones, Natural Diamonds & Real Gold |
|
What is a Genuine Gemstone? Know All About Genuine Gemstones. Read More.
|
|
What is Authentic Jewelry? Know All About Authentic. Read More.
|
|
What is Certified Jewelry? Know All About Certified Jewelry. Read More.
|
|
What is Fine Designer Jewelry? Know All About Fine Jewelry. Read More.
|
|
Genuine Gemstones Identification? Know All About Fine Genuine Gemstones. Read More.
|
|
What is Real Gold, Platinum, Silver, Palladium or Fake Gold Filled, Gold Plated? Know All About Real Gold, Platinum, Silver, Palladium, Platinum, Silver, Palladium. Read More.
|
|
Jewelry Caring & Cleaning, Ruby Jewelry Caring & Cleaning, Sapphire Jewelry Caring & Cleaning, Emerald Jewelry Caring & Cleaning, Diamond Caring & Cleaning. Read More.
|
|
Genuine Diamond Testers, Genuine Gemstones Testers, Real Metal Testers, Authentic Jewelry Testers. ? Know All About Testers to Identify Natural Diamonds, Genuine Gemstones, Real Metals and Authentic Jewelry. Read More.
|
| Sndgems Jewelry Trade Affiliations, Read More and Conflict-Free Diamonds. Read More. |
| Celebrity News - Red Carpet, Oscars, Celebrity Jewelry. Read More. |
| Fine-Quality Burma Ruby, Ceylon Ruby, Kashmir Sapphire, Burma Sapphie, Columbian Emerald Guides. Read More. |
| Complete Online Shopping Guide to ensure safe shopping, getting quality value product with money back guarantee when shopping online for jewelry. Read More. |
|
Identification of Synthetic or Fake Emeralds from Genuine Emeralds Guidelines. Read More.
|
|
Identification of Synthetic or Fake Rubies and Sapphires from Genuine Rubies and Sapphires Guides. Read More.
|
| Identification of Ruby, Sapphire Sources - If they're from Burma, Ceylon or Thailand. Read More. |
| Identification of Emerald Sources - If they're from Columbia, Zambia, Brazil, Africa. Read More. |
| Gemstone Buying Guides - How to Evaluate, Identify & Select Genuine Gemstones of Good Quality. Read More. |
|
Gemology 101: Gemologists Identification & Valuation of Gemstones Diamonds. Read More.
|
|
Identification of Synthetic or Fake Imitation Diamonds from Genuine Diamonds Buying Guides. Read More.
|
|
Jewelry Appraisal Education Center - What's Your Jewelry Worth? Jewelry Appraisal, Diamond and Gemstone Appraisals Guidance. Authentic Jewelry: Certified Diamond & Genuine Gemstone Jewelry. Read More.
|
|
Learn about Diamond Ring Styles and Designs – Choose your Perfect Engagement Ring, Anniversary Ring or Wedding Ring. Learn More.
|
| Jewelry as a gift for your Man – An elaborate Men’s Jewelry Buying Guide. Read More. |
|
The Worlds Top Jewelry Stores, Online Shopping Guides. Read More.
|
| Complete Online Shopping Guide to ensure safe, secure online jewelry shopping. Read More. |
|
|

























